
📘 Course Information
- Course Name: Algorithmic Problem Solving
- Course Code: 23ECSE309
- Name: Karthik Jodangi
- University: KLE Technological University, Hubballi-31
📝 Overview
This portfolio explores the functionalities of Over-The-Top (OTT) platforms, analyzing existing features and proposing new functionalities to enhance user experience and operational efficiency. The document covers market analysis, business use cases, potential challenges, suitable algorithms, and performance analysis.
📑 Table of Contents
Introduction
Over-The-Top (OTT) platforms have revolutionized how we access and enjoy media content in the digital age. Services like Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, and Disney+ deliver a vast array of movies, series, and original programming directly to viewers over the internet, circumventing traditional broadcast methods. At the heart of these platforms lie sophisticated algorithms that drive personalized user experiences and operational efficiency.
Algorithms play a pivotal role in every aspect of OTT platforms, from content recommendation and user interface customization to real-time streaming optimization. By analyzing user data such as viewing habits, preferences, and interactions, these algorithms tailor content suggestions to individual tastes. For instance, collaborative filtering algorithms identify viewing patterns and similarities among users to suggest relevant content, while adaptive streaming algorithms adjust video quality based on network conditions, ensuring smooth playback experiences.
Moreover, algorithms enable OTT platforms to enhance monetization strategies through targeted advertising and dynamic pricing models. By leveraging data insights, platforms can deliver personalized ads that resonate with viewers, thereby maximizing engagement and revenue potential.
In summary, algorithms are the driving force behind the success of OTT platforms, empowering them to deliver compelling content experiences while continually evolving to meet the diverse needs of modern audiences.
Market Analysis
OTT platforms have significantly transformed the content consumption landscape. The global OTT market, valued at USD 121.61 billion in 2021, is projected to grow at a CAGR of 29.4% from 2022 to 2030. Major players include Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, Hulu, and Disney+. The growth is driven by increasing internet penetration and the adoption of smart devices.
Objectives
- Identify and analyze existing OTT platform functionalities.
- Propose new functionalities to enhance the domain.
- Explore business use cases, challenges, and benefits.
- Suggest suitable algorithms and design techniques.
Business Cases
Existing Functionalities
- 📺 Content Streaming
- 🔄 Personalized Recommendations
- 📱 Multiple Device Compatibility
- 📥 Offline Viewing
- 📂 Content Categorization
- 👤 User Profiles
- 📜 Content Licensing and Rights Management
- 💰 Content Monetization
- 🌐 Content Delivery Network
- 🗣 Social Integration
Proposed Functionalities
- 🔍 Content Discovery Tools
- Advanced Filtering Options
- Personalized Playlists
- Mood-Based Recommendations
- 🛡 Measures Against Piracy and Unauthorized Access
- 🕶 AR and VR Technologies
- 👥 Social Viewing Experiences
- Virtual Watch Parties
- Real-time Chat
- 🎯 Personalized Advertising
- 🏠 Integration with Smart Home Devices
- 🌎 Content Localization
- Volume Adjustment for BGM, Voice, and Songs
- Multi-language Support
- AI-generated Subtitles and Dubbing
- 📊 Interactive Content
- Quizzes, Polls, etc.
- Advanced Content Management
- Content Recommendation Engine, Dynamic Content Adaptation, Predictive Content Analytics
Detailed Business Use Cases
- Advanced Filtering Options
- Challenge: Efficiently filtering a large dataset of content.
- Algorithm: Trie Data Structure.
- Description: A Trie is a tree-like data structure used to store a dynamic set of strings where keys are usually strings. It is useful for search and filter functionalities where prefix matching is needed.
- Find the sample code here
-
Personalized Playlists
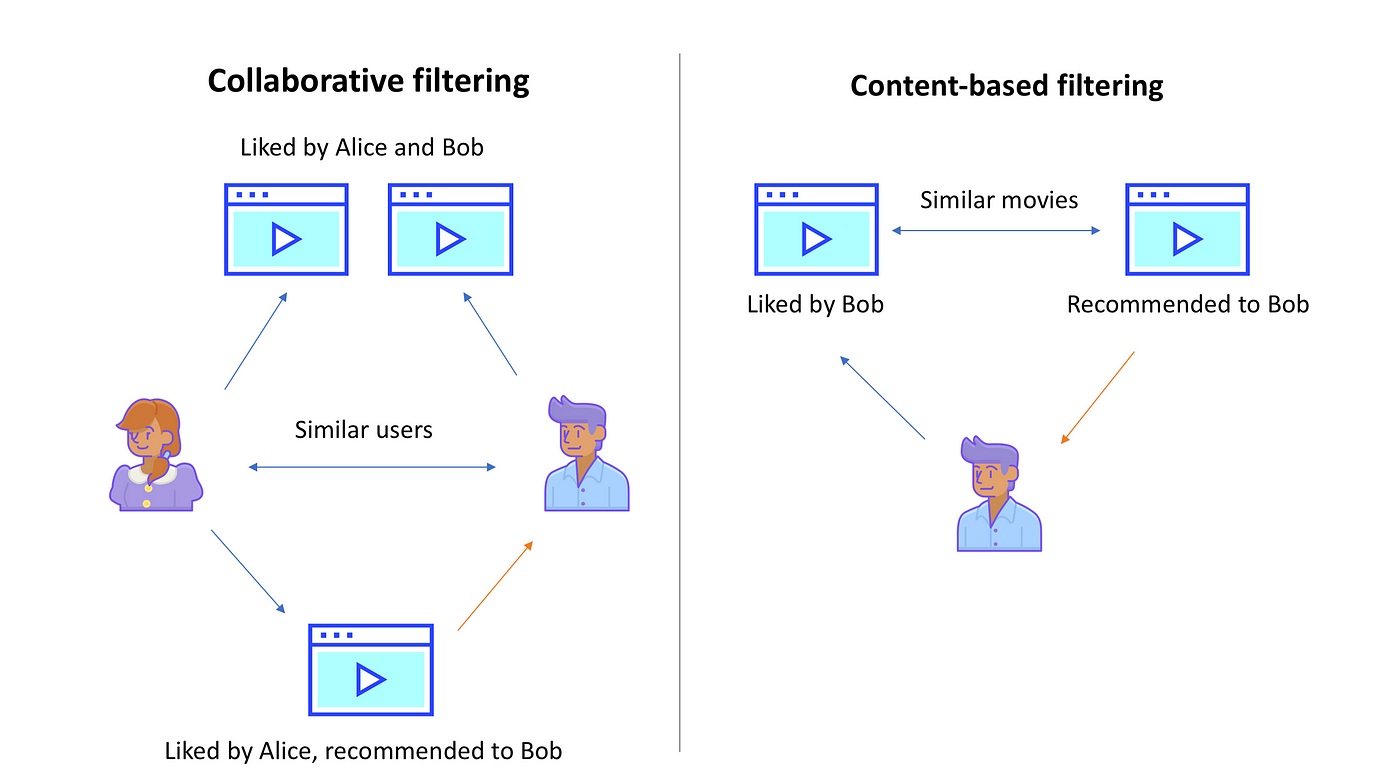
- Challenge: Creating playlists based on user preferences.
- Algorithm: Collaborative Filtering.
- Description: Collaborative Filtering algorithms, such as user-based or item-based approaches, are well-suited for recommending playlists based on similarities between users or between playlists themselves.
- Find the sample code here
- Mood-Based Recommendations
- Challenge: Accurately identifying user mood.
- Algorithm: Sentiment analysis using NLP techniques.
- Description: Utilizing sentiment analysis techniques to analyze user reviews, comments, or social media interactions related to content can provide insights into mood and preferences.
- Find the sample code here
- Measures Against Piracy
- Challenge: Preventing unauthorized access and distribution.
- Algorithm: Watermarking and encryption.
- Description: Strong encryption algorithms like AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) to protect the content itself from being accessed without authorization.
- Find the sample code here
-
AR and VR Technologies
- Challenge: Creating immersive content experiences.
- Algorithm: 3D rendering and real-time processing.
- Description: Rasterization: Commonly used for real-time rendering in VR and AR applications. Ray Tracing: Provides more realistic lighting and shadows.
-
Virtual Watch Parties

- Challenge: Synchronizing content playback for multiple users.
- Algorithm: Vector clocks and consensus algorithms.
- Description: Ensure real-time communication, playback synchronization, and efficient session management.
- Real-time Chat
- Challenge: Seamless user interaction.
- Algorithm: Message queues, pub/sub pattern, WebSockets.
- Description: Facilitate responsive and scalable real-time chat experiences.
- Personalized Advertising
- Challenge: Targeting ads effectively without intruding on user experience.
- Algorithm: Machine learning algorithms.
- Description: Decision Trees and Random Forests predict user preferences based on demographic data and viewing history.
- Find the sample code here
- Integration with Smart Home Devices
- Challenge: Seamlessly connecting with smart home ecosystems.
- Algorithm: MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport).
- Description: Efficient, reliable communication between OTT platforms and smart home devices.
- Find the sample code here
- Volume Adjustment
- Challenge: Segregated audio for BGM, voice, and songs.
- Algorithm: Finite Impulse Response (FIR) filters, dynamic range compression.
- Description: Adjust volume levels independently for background music (BGM), voice, and songs.
-
Multi-language Support

- Challenge: Availability of different languages for the same viewing content.
- Algorithm: Hash tables, trie data structures, N-gram language models.
- Description: Detect and switch between languages dynamically, presenting localized content based on user preferences.
- AI-generated Subtitles and Dubbing
- Challenge: Real-time automated dubbing and subtitles feature.
- Algorithm: Sequence alignment (e.g., Needleman-Wunsch), machine learning models (e.g., Seq2Seq).
- Description: Automate subtitles and dubbing tasks for multilingual content accessibility.
- Find sample code for Needleman-Wunsh here
- Find sample code for Seq2Seq model here
-
Interactive Content

- Challenge: Enhancing user engagement through interactive features.
- Algorithm: Hash tables, graph algorithms, real-time data processing.
- Description: Implement quizzes, polls, and interactive pathways for engaging user experiences.
- Content Recommendation Engine
- Challenge: Enhancing the accuracy of content recommendations.
- Algorithm: Machine learning algorithms (e.g., collaborative filtering, neural networks).
- Description: Leveraging user behavior data and content metadata to personalize recommendations, improving user engagement and retention.
- Dynamic Content Adaptation
- Challenge: Optimizing content delivery across varying network conditions.
- Algorithm: Adaptive bitrate streaming algorithms (e.g., MPEG-DASH, HLS).
- Description: Adjusting video quality dynamically based on available bandwidth and device capabilities to ensure smooth playback and minimize buffering.
- Predictive Content Analytics
- Challenge: Forecasting viewer preferences and content trends.
- Algorithm: Time series analysis, predictive modeling.
- Description: Analyzing historical viewer data and market trends to predict popular content genres and optimize content acquisition and scheduling.
Performance Analysis
Advanced Filtering Options
- Algorithm Used: Trie Data Structure
- Time Complexity:
- Insertion: O(L)
- Search: O(L)
- Space Complexity: O(ALPHABET_SIZE * L * N)
Personalized Playlists
- Algorithm Used: Collaborative Filtering
- Time Complexity:
- Depends on the specific approach (e.g., user-based vs item-based).
- Typically involves matrix operations with complexity ranging from O(N^2) to O(N^3).
- Space Complexity:
- Depends on the size of the user-item matrix.
Mood-Based Recommendations
- Algorithm Used: Sentiment Analysis using NLP Techniques
- Time Complexity:
- Depends on the complexity of the sentiment analysis model.
- Typically involves processing text with complexity ranging from O(N) to O(N^2).
- Space Complexity:
- Depends on the size of the sentiment analysis model and input data.
Measures Against Piracy
- Algorithm Used: Watermarking and Encryption
- Time Complexity:
- Encryption (e.g., AES): O(N)
- Watermarking: Depends on the watermarking technique used.
- Space Complexity:
- Depends on the size of the content and the encryption keys.
AR and VR Technologies
- Algorithm Used: 3D Rendering and Real-Time Processing
- Time Complexity:
- Rasterization: Typically O(N) to O(N^2) depending on scene complexity.
- Ray Tracing: O(N^3) or higher, depending on scene complexity and desired quality.
- Space Complexity:
- Memory-intensive for storing 3D models and textures.
Virtual Watch Parties
- Algorithm Used: Synchronization Algorithms (e.g., Vector Clocks)
- Time Complexity:
- Depends on the specific synchronization algorithm used.
- Typically involves operations with complexity ranging from O(N) to O(N^2) depending on the number of participants.
- Space Complexity:
- Depends on the size of data structures used for maintaining session state.
Real-time Chat
- Algorithm Used: Message Queues, Pub/Sub Pattern, WebSockets
- Time Complexity:
- Depends on the efficiency of message queue operations and WebSocket connections.
- Space Complexity:
- Memory usage scales with the number of active chat participants and message history.
Personalized Advertising
- Algorithm Used: Machine Learning Algorithms (e.g., Decision Trees, Random Forests)
- Time Complexity:
- Training: Typically O(N * M * log N) to O(N^2 * M), where N is the number of samples and M is the number of features.
- Inference: Depends on the complexity of the model and input data.
- Space Complexity:
- Depends on the size of the training data and model parameters.
Integration with Smart Home Devices
- Algorithm Used: MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport)
- Time Complexity:
- Depends on the efficiency of MQTT message handling and network latency.
- Space Complexity:
- Minimal overhead in terms of memory usage.
Volume Adjustment
- Algorithm Used: Digital Signal Processing (DSP), Finite Impulse Response (FIR) Filters
- Time Complexity:
- DSP operations: Depends on the complexity of signal processing algorithms (typically O(N) to O(N^2)).
- Space Complexity:
- Memory usage scales with the size of audio samples and processing buffers.
Multi-language Support
- Algorithm Used: Hash Tables, Trie Data Structures, N-gram Language Models
- Time Complexity:
- Varies based on the specific algorithm (e.g., O(L) for trie operations, O(N) for language detection using N-grams).
- Space Complexity:
- Depends on the size of language models and data structures used for text storage.
AI-generated Subtitles and Dubbing
- Algorithm Used: Sequence Alignment (e.g., Needleman-Wunsch), Machine Learning Models (e.g., Seq2Seq)
- Time Complexity:
- Depends on the complexity of alignment algorithms (e.g., O(N*M) for Needleman-Wunsch) and training/inference time for machine learning models.
- Space Complexity:
- Memory-intensive for storing model parameters and processing input data.
Interactive Content
- Algorithm Used: Hash Tables, Graph Algorithms, Real-time Data Processing
- Time Complexity:
- Depends on the specific algorithm used (e.g., O(1) for hash table operations, O(N^2) for graph traversal).
- Space Complexity:
- Memory usage scales with the size of interactive content data and active user sessions.
Content Recommendation Engine
- Algorithm Used: Machine Learning Algorithms
- Time Complexity:
- Training: O(N * M * log N) to O(N^2 * M), depending on the model complexity and dataset size.
- Inference: O(M), where M is the number of features.
- Space Complexity:
- Depends on the size of the training data and model parameters.
Dynamic Content Adaptation
- Algorithm Used: Adaptive Bitrate Streaming Algorithms
- Time Complexity:
- Depends on the complexity of bitrate adaptation logic.
- Typically involves real-time decisions based on network conditions and client feedback.
- Space Complexity:
- Minimal, primarily involves memory for buffering and metadata.
Predictive Content Analytics
- Algorithm Used: Time Series Analysis, Predictive Modeling
- Time Complexity:
- Depends on the forecasting model (e.g., ARIMA, LSTM).
- Training and prediction times vary based on data volume and complexity.
- Space Complexity:
- Depends on the size of historical data and model parameters.
References
[1] “Streaming Media” Website, https://www.streamingmedia.com/.
[2] “What is OTT (Over-The-Top) and How Does it Relate to Apps?” Article, https://clevertap.com/blog/ott/.
[3] “The Netflix Recommender System: Algorithms, Business Value, and Innovation” Paper, https://dl.acm.org/doi/pdf/10.1145/2843948
[4] “OPEN SOURCE OTT PLATFORM” Article, https://nexttv.github.io/
[5] “Live Event Streaming Solution” Website, https://www.dacast.com/live-event-streaming
[6] “How Streaming Services use Algorithms” Article https://amt-lab.org/blog/2021/8/algorithms-in-streaming-services
[7] “Netflix Recommendations: Beyond the 5 stars” https://netflixtechblog.com/netflix-recommendations-beyond-the-5-stars-part-1-55838468f429